Definition
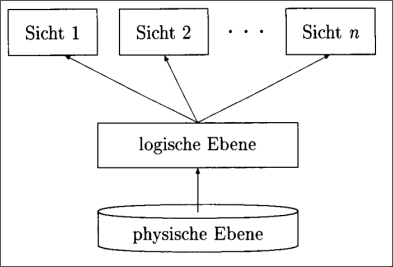
Drei-Ebenen-Architektur
ANSI-SPARC Architecture
The ANSI-SPARC architecture is a three-level architecture for database management systems:
Levels:
- User (External): A user’s view of the database describes a part of the database that is relevant to a particular user. It excludes irrelevant data as well as data which the user is not authorised to access.
- Conceptual (Logical): The conceptual level is a way of describing what data is stored within a whole database is inter-related. The conceptual level does not specify how the data is physically stored.
- Physical (Internal): The physical level involves how the database is physically represented on the computer system. It describes how the data is actually stored in the database and on the computer hardware.
The idea of this abstraction is to make it possible to change the lower levels without affecting the higher levels. For example, the architecture allows for physical data-independence, meaning that if more physical storage is added to the hardware, the conceptual and user level are unaffected.