Definition
Kernel Method
A kernel method is a general strategy used in machine learning to take learning algorithms that only work linearly (like the perceptron or the standard SVM) and upgrade them to solve non-linear problems efficiently.
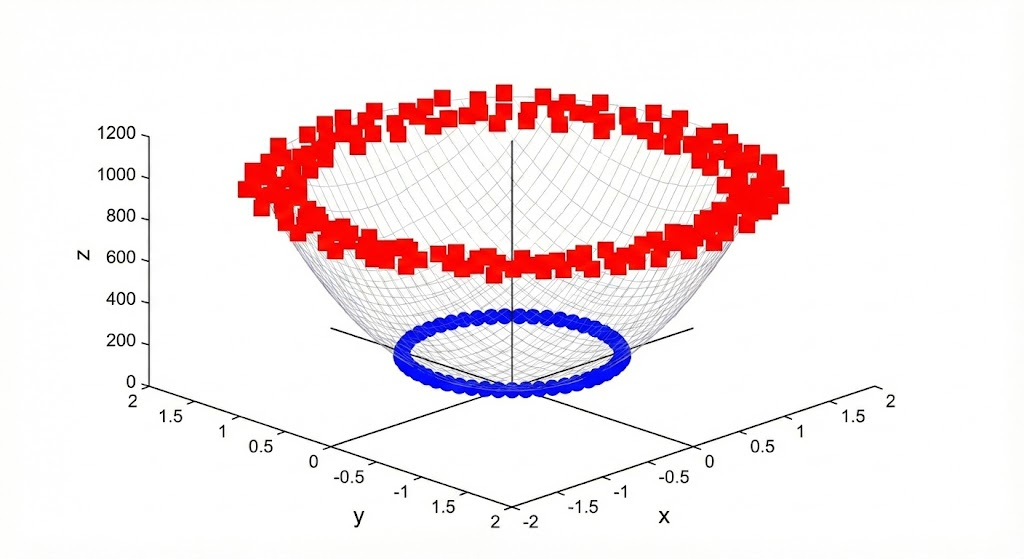
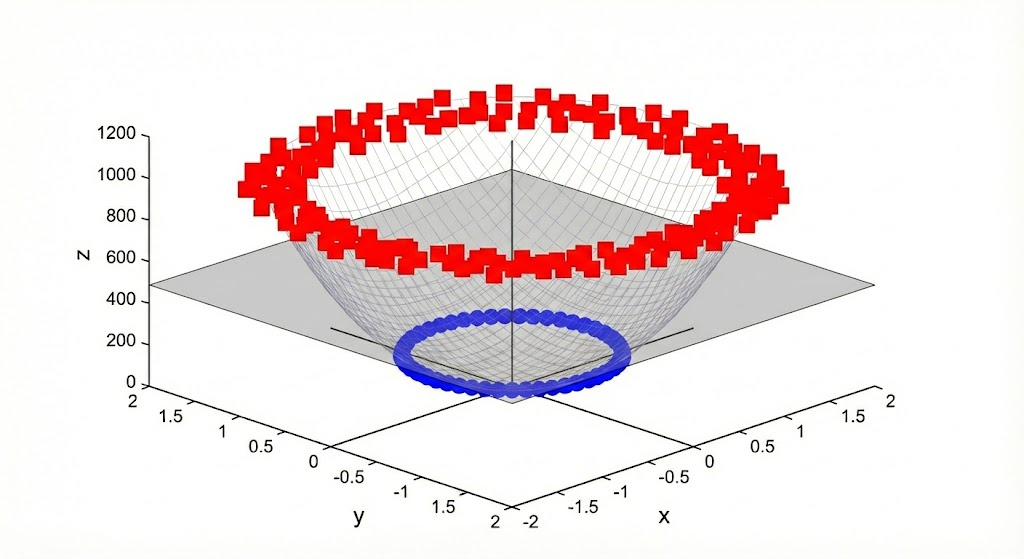
If you can’t separate the data in its current space (the input space), map it into a higher-dimensional universe (the feature space), which is done via a feature map function :
The Curse of Dimensionality
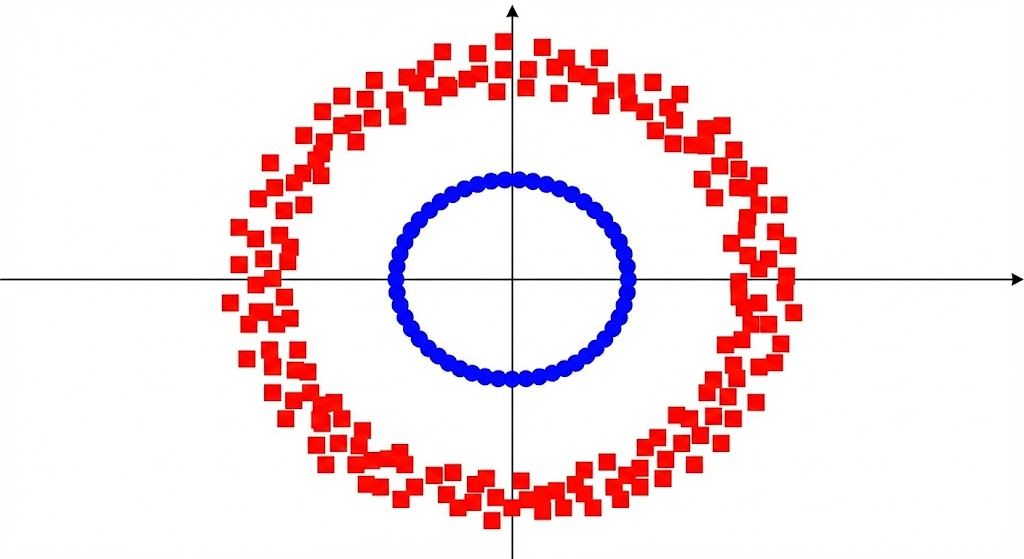
If higher dimensional data leads to higher separability, why not map data to a billion dimensions, or even more?
The Curse of Dimensionality: Calculating the explicit transformation for every data point can be incredibly slow and memory-intensive. Sometimes the target space is even infinite-dimensional, making direct calculation impossible.
Definition
Link to originalCurse of Dimensionality
The curse of dimensionality refers to various phenomena that arise when analysing and organising data in high-dimensional spaces that do not occur in low-dimensional settings. Formally, as the dimensionality increases, the volume of the space grows exponentially, causing the available data points to become sparse.
Kernel Trick
Many linear learning algorithms don’t actually need to see the data points themselves. They only ever need to know the angles and distances between pairs of data points. This means that the algorithm only depends on the inner product between points.
Existence of a Feature Map
There exists a feature map from the instance space into a Hilbert space such that:
If we were to map the data to high dimensions, the algorithm would need the inner product in that new space:
Definition
Link to originalKernel Function
A kernel function is a symmetric, positive semi-definite function that computes the inner product of two data points in a high-dimensional Hilbert space without requiring the explicit computation of the feature mapping . Formally: