Definition
Recoverable Schedule (ACID)
A schedule is recoverable if for each pair of transactions , where reads data items written by , must commit before .
Examples
Recoverable Schedule Example
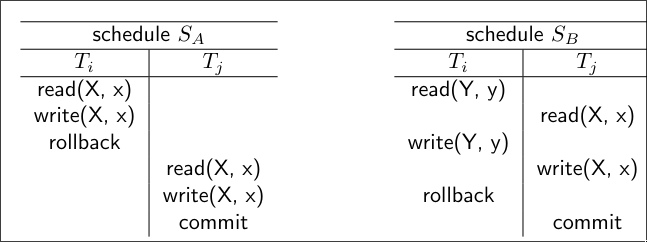
Irrecoverable Schedule Example
| Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | write() | 100 (uncomitted) | |
| 2 | read() | 100 | |
| 3 | commit | ||
| 4 | abort |
In this scenario:
- writes a value to data item . This value is not yet committed and resides in a memory buffer.
- reads the uncommitted value of written by . This is a dirty read.
- then commits its changes. Since has committed, its results are now considered permanent.
- Subsequently, fails for some reason and must be aborted. The system needs to roll back the changes made by .
The problem here is that , which has already committed, based its operations on a value from transaction that never successfully completed. The value of read by is now effectively a “ghost” value. Since has committed, we cannot simply roll it back. This leads to an inconsistent database state.