Definition
Logarithmic Scale
In a Cartesian coordinate system, sometimes, one or more axes are log-scaled, meaning that the points are logarithmically aligned.
Values
Negative Values
Since is not defined for negative values, log-scaled axes can only represent positive values.
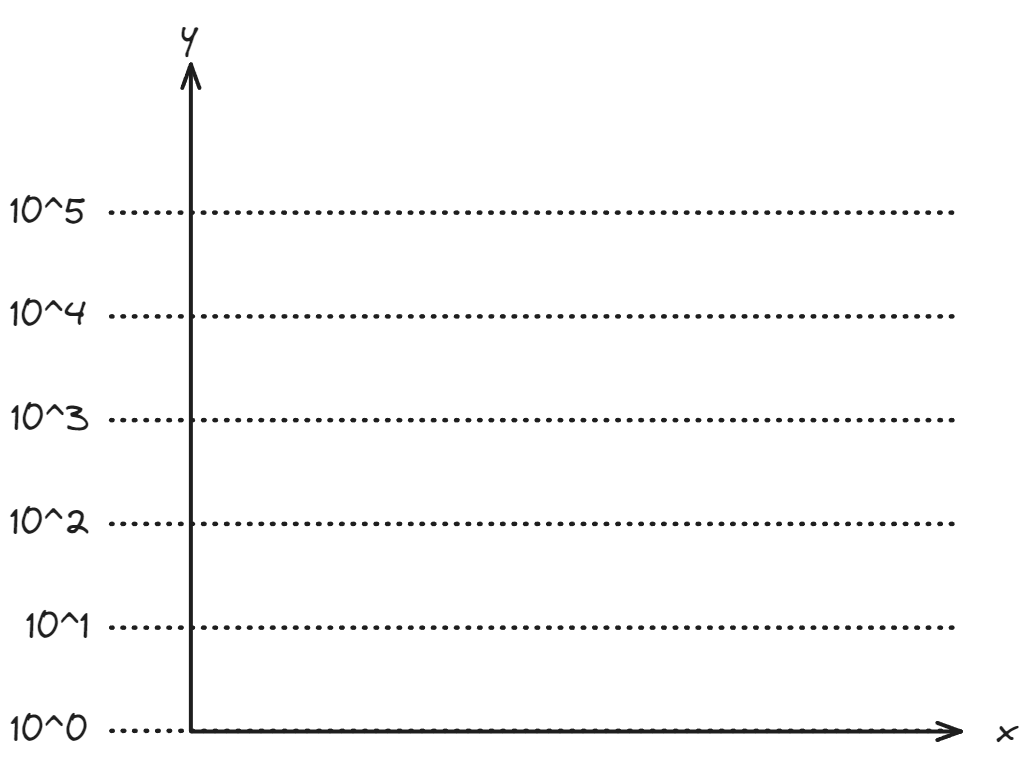
, which is equal to 1, is the -line which is why negative values cannot be .
Values between 0 and 1
However, values between (0 and 1 excluded) are represented in the -line:
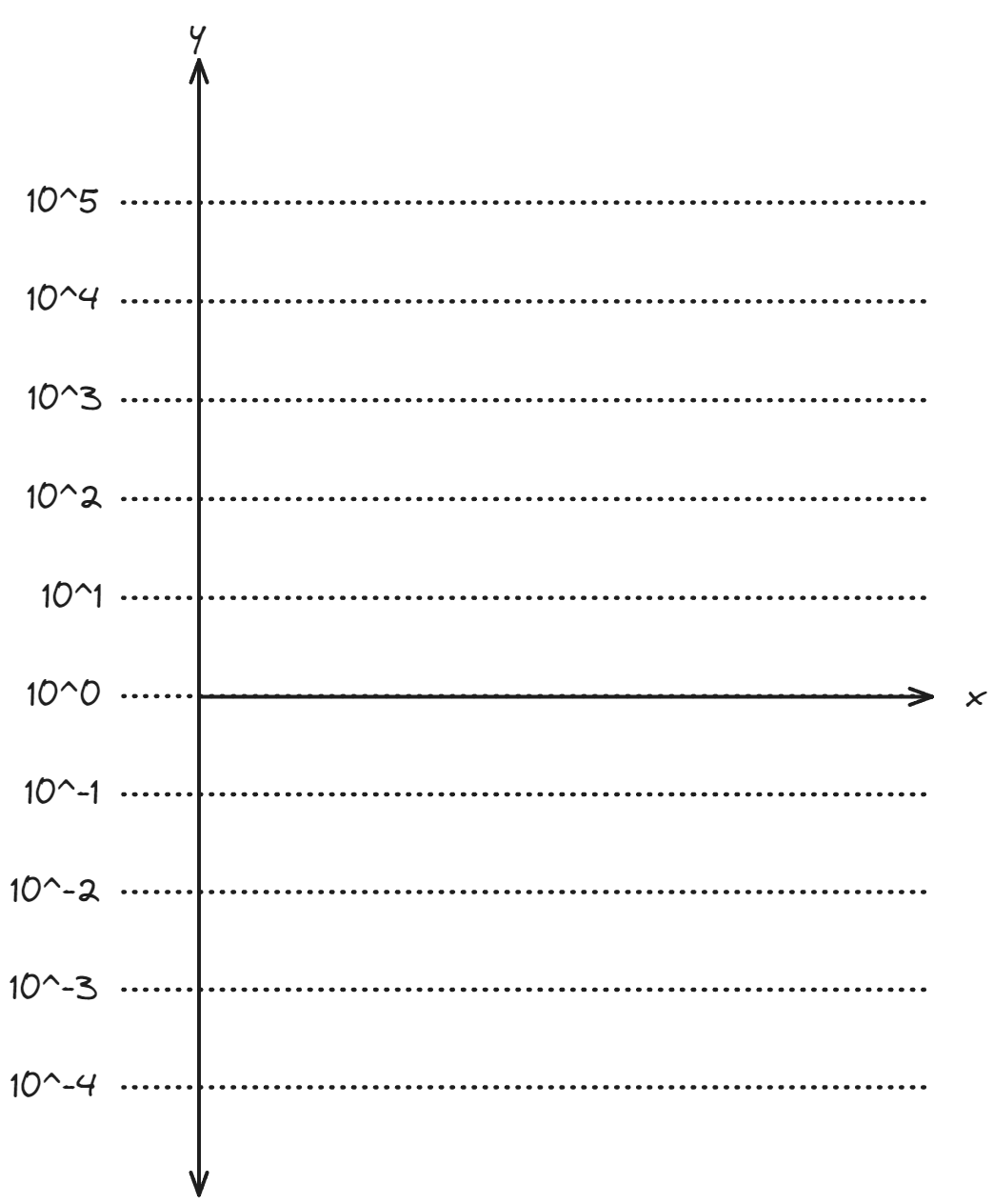
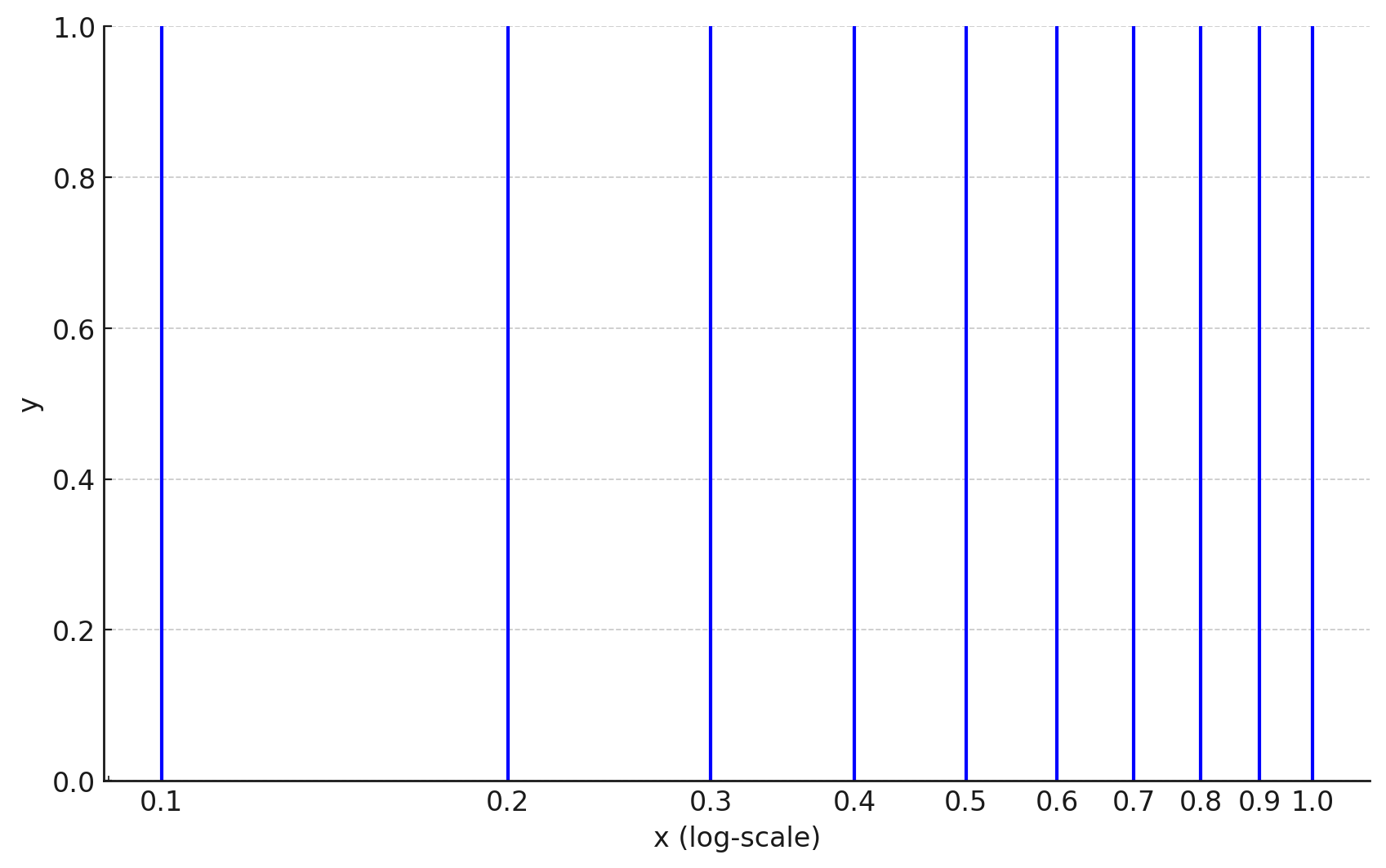
Values between Integers
Example: The difference is smaller than . Therefore, the log-values are not equidistant.
Log-Scale for Y:

Log-Scale for X:
Types
X Axis only
Logarithm functions appear as a straight line in a -log coordinate system.

Y Axis only
In a -log coordinate system, exponential functions are represented as straight lines.
Why is it a Straight Line?
Applying the logarithm to an exponential function :
Let and , the equation can be formulated as:
Which is a linear function. Therefore, -logscaled exponential functions are linear functions.

Both axes: X and Y
Power functions appear as a straight line in -logscaled coordinate systems.