Definition
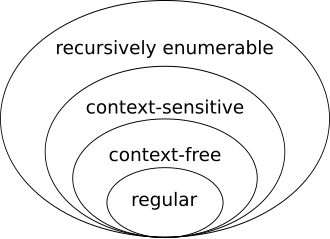
Type 0
Definition
Link to originalGrammar
A grammar is a 4-tuple:
where:
- is the finite set of non-terminal symbols
- is the finite set of terminal symbol ()
- are the product rules
- is the start symbol
Denote:
- instead of
- instead of
Further, is also called unconstrained grammar or type- grammar.
Type 1
Definition
Link to originalContext-Sensitive Grammar (Type-1)
A grammar is called context-sensitive (Type-1) if every production in is of the form where there exist , , and such that
In words: a single nonterminal may be replaced by a nonempty string , but only in its surrounding context .
Type 2
Definition
Link to originalContext-Free Grammar (Type-2)
A grammar is called context-free (Type-2) if every production in is of the form
where and .
That is, the left-hand side of every production consists of a single nonterminal.A language is called context-free there exists a pushdown automaton that accepts it.
From the start symbol, non-terminal symbols are iteratively replaced by applying the respective production rules.
Type 3
Definition
Link to originalRegular Grammar (Type-3)
A grammar is called regular (Type-3) if every production in is of one of the forms
where , , and is the empty word.
Such a grammar (right-linear) generates exactly the regular languages.